自己实现一个简单的Spring容器
为什么要手写:
1提升编码质量与水准
2可借鉴框架开发与设计思想
3代码重构提供参考依据
手写后会怎样
透彻理解代码的实现原理
提高解决问题的效率
锻炼自己造轮子的能力
经典问题
1 什么是Spring框架,Spring框架有哪些主要模块?
2 使用Spring框架能带来哪些好处?
3 什么是控制反转?
4 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext有什么区别?
5 请解释Spring Bean的生命周期
6 Spring Bean的各种作用于之间有什么区别?
7 Spring框架中的单例Beans是线程安全的吗?
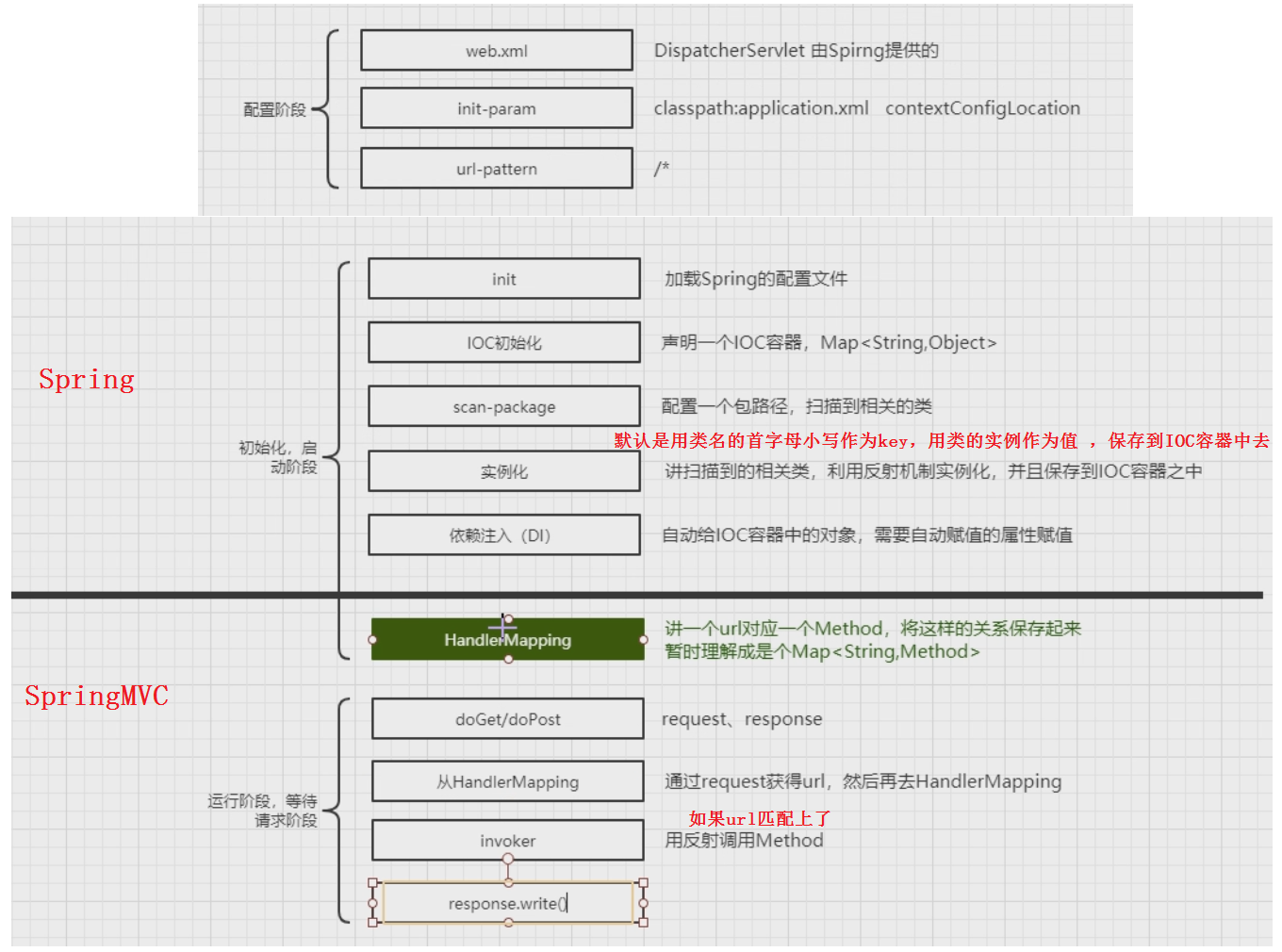
默认是用类名的首字母小写作为key,用类的实例作为值 ,保存到IOC容器中去
实战
下面的代码还没有实现handlerMapping,但是对加载配置文件, 注解的扫描, bean实例化, 把bean塞入ioc容器 ,autowired都实现了
package org.rico.learnSpring.framework.webmvc.servlet;
import org.rico.learnSpring.framework.annotation.MyAutowired;
import org.rico.learnSpring.framework.annotation.MyController;
import org.rico.learnSpring.framework.annotation.MyService;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by Rico on 2018/11/11.
*/
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet{
private Properties contextConfig=new Properties();
private List<String> classNames=new ArrayList<String>();
private Map<String,Object> ioc=new HashMap<String,Object>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//从这里开始启动SpringMVC
//1 加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2 扫描所有相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//3 初始化所有扫描到的类
try {
doInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4 自动注入
doAutowired();
//*******Spring到此初始化完成*********************************
//*******以下属于SpringMVC的内容*****************************
//5 初始化HandlerMapping
initHandlerMapping();
System.out.println("MySpring init end");
}
//载入配置
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
InputStream is=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(is!=null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//扫描类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage){//传入的参数是哪些包需要扫描的
URL url= this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"+scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.","/"));//把点替换成斜杠
File classDir=new File(url.getFile());//拿到这个包下面的所有class
for(File file : classDir.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){//如果是文件夹,还需要继续搜寻,递归调用自身
doScanner(scanPackage+"."+file.getName());//递归
}else{//如果不是文件夹
String className=scanPackage+"."+file.getName().replace(".class","");//把.class这个后缀去掉
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
//实例化扫描到的类
private void doInstance() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
if(classNames.isEmpty()){return;}
for(String className:classNames){
try {
Class<?> clazz=Class.forName(className);//拿到class类
//不是所有的类都要实例化,只实例化加了注解的类
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
//把类初始化,然后放到IOC容器中
//key是类名首字母小写
String beanName=lowerFirstCase(clazz.getName());
ioc.put(beanName,clazz.newInstance());
}else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyService.class)){//如果是Service注解
//默认采用首字母
//自定义bean的name,优先使用自定义的名字
//根据接口类型来赋值(接口不能实例化,但是接口的实现类可以实例化)
MyService service= clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class);//拿到这个类上的@MyService注解
String beanName=service.value();
if("".equals(beanName.trim())){//如果beanName是空的话,那么说明用户没有自定义beanName,那么就用首字母小写作为beanName
beanName=lowerFirstCase(clazz.getName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName,instance);//将其放入ioc
for(Class<?> i:clazz.getInterfaces()){//获取这个类的接口 如果这个类有多个接口,那么需要报错,这里没做
ioc.put(i.getName(),instance);//key是这个接口的名称
//疑问,这个接口名不需要首字母小写作为key吗?
}
//所以有可能出现这种情况,就是以这个interface作为key的有一个实例,以类首字母小写作为key也有一个实例,且实例是同一个,主要是为了满足用户不同的注入要求
}else{
continue;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//注入
private void doAutowired() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){return;}
//循环IOC容器中所有类,然后对需要自动赋值的属性进行赋值
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:ioc.entrySet()){
//依赖注入,不管是谁,只要加了@MyAutowired注解的都要注入,哪怕它是私有的,哪怕他是受保护的.为什么?是因为反射破坏了它的封装性,在反射面前,所有东西都是裸露的. 所以反射要慎用,一般在框架里或者底层的设计模式中使用
Field[] fields=entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();//获取所有的字段
for(Field field:fields){//找出有@MyAutowired的注解的字段
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)){ continue; }
MyAutowired autowired=field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class);
String beanName=autowired.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName)){//如果没有指定引用那个bean,那么就是它的类型的那个bean
beanName=field.getType().getName();
}
//暴力访问
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(),ioc.get(beanName));//给这个字段复制,第一个参数是这个字段所在的对象实例,第二个参数就是具体的值
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
}
private void initHandlerMapping() {
}
//首字母小写工具类
private String lowerFirstCase(String str){
String firstString=str.substring(0, 1);
firstString=firstString.toLowerCase();
String left=str.substring(1,str.length());
return firstString+left;
}
}
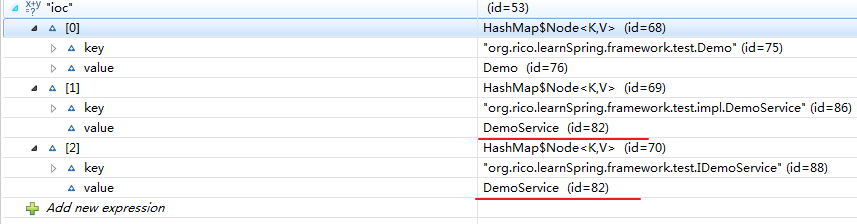
这里明明代码只写了2个注解,一个是Controller,一个是Service,怎么有三个bean?
是因为把service的实现和接口都作为了一个bean的key,这样不管是用接口去注入还是用实现去注入都可以注入成功
接下来实现initHandlerMapping方法
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()) {return; }
//扫描所有的bean
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()){
//找到注解在类上的RequestMapping,拿到它的值
Class<?> clazz=entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){continue;}//只针对Controller,如果不是Controller,加了RequestMapping就忽略
String baseUrl="";//类上注解的requestMapping,是基url
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
MyRequestMapping requestMapping=clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl=requestMapping.value();
}
//扫描所有的公共方法
for(Method method:clazz.getMethods()){
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){ continue; }
MyRequestMapping myRequestMapping=method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
String methodUrl=("/"+baseUrl+myRequestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+","/");//把连续的斜杠处理成单个斜杠
handlerMapping.put(methodUrl,method);
System.out.println("Mapping :"+methodUrl+","+method);//打印日志
}
}
}
测试类
@MyController
@MyRequestMapping("/demo")
public class Demo {
@MyAutowired
private IDemoService demoService;
@MyRequestMapping("/query")
public void query(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @MyRequestParam("name") String name){
String result=demoService.get(name);
try{
response.getWriter().write(result);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出

接下来实现doGet doPost
private Map<String,Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String,Method>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//this.doGet(req, resp);
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//super.doPost(req, resp);
doDispatch(req,resp);
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
String url=req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath=req.getContextPath();
url=url.replaceAll(contextPath,"").replaceAll("/+","/");//把多余的斜杠替换掉
if(!handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) {//如果url在handlerMapping没有的话就返回404
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>404 not found</h1> --By Rico");
return;
}
Method method=handlerMapping.get(url);//拿到这个url对应的方法
method.invoke(这里遇到了问题)//第一个参数是谁调这个方法,第二个参数就是方法参数
System.out.println(method);
}
到此,除了调用哪个url对应的method,其他步都完成了,比如url请求处理
当请求到了该url会打印这个方法
不存在的url会404
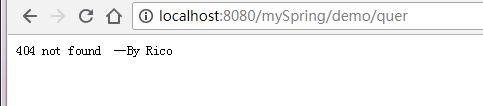
但是此时在调用method.invoke的时候出了问题,因为调用那个method的bean被弄丢了,所以handlerMapping不能用map,得改下,把那个bean也纳入进来了
修改后的完整的MyDispatcherServlet的代码
package org.rico.learnSpring.framework.webmvc.servlet;
import org.rico.learnSpring.framework.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* Created by Rico on 2018/11/11.
*/
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet{
private Properties contextConfig=new Properties();
private List<String> classNames=new ArrayList<String>();
private Map<String,Object> ioc=new HashMap<String,Object>();
//private Map<String,Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String,Method>();
private List<Handler> handlerMapping=new ArrayList<Handler>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//this.doGet(req, resp);
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//super.doPost(req, resp);
try {
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
try{
Handler handler=getHandler(req);
if(handler==null){//如果没有匹配
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>404 not found</h1> --By Rico");
return;
}
//获取方法的参数列表
Class<?> [] paramTypes=handler.method.getParameterTypes();
//保存所有需要自动赋值的参数值
Object[] paramValues=new Object[paramTypes.length];
Map<String,String[]> params=req.getParameterMap();
for(Map.Entry<String,String[]> param:params.entrySet()){
String value=Arrays.toString(param.getValue()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]","").replaceAll("//","/");
//如果找到匹配的对象,则开始填充参数值
if(!handler.paramIndexMapping.containsKey(param.getKey())){continue;}
int index=handler.paramIndexMapping.get(param.getKey());
paramValues[index]=convert(paramTypes[index],value);
}
//设置方法中的request和response对象
int reqIndex=handler.paramIndexMapping.get(HttpServletRequest.class.getName());
paramValues[reqIndex]=req;
int respIndex=handler.paramIndexMapping.get(HttpServletResponse.class.getName());
paramValues[respIndex]=resp;
handler.method.invoke(handler.controller,paramValues);//反射调用
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}
/*
String url=req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath=req.getContextPath();
url=url.replaceAll(contextPath,"").replaceAll("/+","/");//把多余的斜杠替换掉
if(!handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) {//如果url在handlerMapping没有的话就返回404
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>404 not found</h1> --By Rico");
return;
}
Method method=handlerMapping.get(url);//拿到这个url对应的方法
method.invoke()//第一个参数是谁调这个方法,第二个参数就是方法参数
System.out.println(method);*/
}
//从HttpServletRequest中通过url匹配handlermapping这个map中的元素来获取handler
private Handler getHandler(HttpServletRequest req)throws Exception{
if(handlerMapping.isEmpty()){return null;}
String url=req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath=req.getContextPath();
url=url.replaceAll(contextPath,"").replaceAll("/+","/");//把多余的斜杠替换掉
for(Handler handler:handlerMapping){
try{
Matcher matcher=handler.pattern.matcher(url);//通过正则匹配url
//如果没有匹配上 继续下一个匹配
if(!matcher.matches()){continue;}
return handler;
}catch (Exception e){
throw e ;
}
}
return null;
}
private Object convert(Class<?> type,String value){
if(Integer.class==type){
return Integer.valueOf(value);
}
return value;
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//从这里开始启动SpringMVC
//1 加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2 扫描所有相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//3 初始化所有扫描到的类
try {
doInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4 自动注入
doAutowired();
//*******Spring到此初始化完成*********************************
//*******以下属于SpringMVC的内容*****************************
//5 初始化HandlerMapping
initHandlerMapping();
System.out.println("MySpring 初始化完成!");
}
//载入配置
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
InputStream is=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(is!=null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//扫描类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage){//传入的参数是哪些包需要扫描的
URL url= this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"+scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.","/"));//把点替换成斜杠
File classDir=new File(url.getFile());//拿到这个包下面的所有class
for(File file : classDir.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){//如果是文件夹,还需要继续搜寻,递归调用自身
doScanner(scanPackage+"."+file.getName());//递归
}else{//如果不是文件夹
String className=scanPackage+"."+file.getName().replace(".class","");//把.class这个后缀去掉
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
//实例化扫描到的类
private void doInstance() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
if(classNames.isEmpty()){return;}
for(String className:classNames){
try {
Class<?> clazz=Class.forName(className);//拿到class类
//不是所有的类都要实例化,只实例化加了注解的类
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
//把类初始化,然后放到IOC容器中
//key是类名首字母小写
String beanName=lowerFirstCase(clazz.getName());
ioc.put(beanName,clazz.newInstance());
}else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyService.class)){//如果是Service注解
//默认采用首字母
//自定义bean的name,优先使用自定义的名字
//根据接口类型来赋值(接口不能实例化,但是接口的实现类可以实例化)
MyService service= clazz.getAnnotation(MyService.class);//拿到这个类上的@MyService注解
String beanName=service.value();
if("".equals(beanName.trim())){//如果beanName是空的话,那么说明用户没有自定义beanName,那么就用首字母小写作为beanName
beanName=lowerFirstCase(clazz.getName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName,instance);//将其放入ioc
for(Class<?> i:clazz.getInterfaces()){//获取这个类的接口 如果这个类有多个接口,那么需要报错,这里没做
ioc.put(i.getName(),instance);//key是这个接口的名称
//疑问,这个接口名不需要首字母小写作为key吗?
}
//所以有可能出现这种情况,就是以这个interface作为key的有一个实例,以类首字母小写作为key也有一个实例,且实例是同一个,主要是为了满足用户不同的注入要求
}else{
continue;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//注入
private void doAutowired() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){return;}
//循环IOC容器中所有类,然后对需要自动赋值的属性进行赋值
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:ioc.entrySet()){
//依赖注入,不管是谁,只要加了@MyAutowired注解的都要注入,哪怕它是私有的,哪怕他是受保护的.为什么?是因为反射破坏了它的封装性,在反射面前,所有东西都是裸露的. 所以反射要慎用,一般在框架里或者底层的设计模式中使用
Field[] fields=entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();//获取所有的字段
for(Field field:fields){//找出有@MyAutowired的注解的字段
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAutowired.class)){ continue; }
MyAutowired autowired=field.getAnnotation(MyAutowired.class);
String beanName=autowired.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName)){//如果没有指定引用那个bean,那么就是它的类型的那个bean
beanName=field.getType().getName();
}
//暴力访问
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(),ioc.get(beanName));//给这个字段复制,第一个参数是这个字段所在的对象实例,第二个参数就是具体的值
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
}
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()) {return; }
//扫描所有的bean
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()){
//找到注解在类上的RequestMapping,拿到它的值
Class<?> clazz=entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){continue;}//只针对Controller,如果不是Controller,加了RequestMapping就忽略
String baseUrl="";//类上注解的requestMapping,是基url
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
MyRequestMapping requestMapping=clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl=requestMapping.value();
}
//扫描所有的公共方法
for(Method method:clazz.getMethods()){
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){ continue; }
MyRequestMapping myRequestMapping=method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
//String methodUrl=("/"+baseUrl+myRequestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+","/");//把连续的斜杠处理成单个斜杠
//handlerMapping.put(methodUrl,method);
String regex=("/"+baseUrl+myRequestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+","/");//把连续的斜杠处理成单个斜杠
Pattern pattern=Pattern.compile(regex);//用了正则之后requestmapping就可以用正则的语法啦,例如/query* 表示query开头的都进行拦截
handlerMapping.add(new Handler(pattern,entry.getValue(),method));//handler类型的构造函数的参数 第一个是正则 第二个是controller对象 第三个是方法Method
System.out.println("Mapping :"+regex+","+method);//打印日志
}
}
}
//首字母小写工具类
private String lowerFirstCase(String str){
String firstString=str.substring(0, 1);
firstString=firstString.toLowerCase();
String left=str.substring(1,str.length());
return firstString+left;
}
private class Handler{
protected Object controller;//保存方法对应的实例
protected Method method;//保存映射的方法
protected Pattern pattern;
protected Map<String,Integer> paramIndexMapping;//参数顺序
protected Handler(Pattern pattern,Object controller,Method method){
this.controller=controller;
this.method=method;
this.pattern=pattern;
paramIndexMapping=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
putParamIndexMapping(method);
}
private void putParamIndexMapping(Method method) {
//提取方法中加了注解的参数
Annotation[][] pa=method.getParameterAnnotations();//它返回的是个二维数组
for(int i=0;i<pa.length;i++){
for(Annotation anno:pa[i]){
if(anno instanceof MyRequestParam){//就是找那个标注了MyRequestParam的注解的参数
String paramName=((MyRequestParam)anno).value();
if(!"".equals(paramName.trim())){
paramIndexMapping.put(paramName,i);
}
}
}
}
//提取方法中的request和response参数
Class<?> [] paramTypes=method.getParameterTypes();
for(int i=0;i<paramTypes.length;i++){
Class<?> type=paramTypes[i];
if(type==HttpServletRequest.class||type==HttpServletResponse.class){
paramIndexMapping.put(type.getName(),i);
}
}
}
}
}
成功
目录结构
源码待上传github
This blog is under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 Unported License
本文链接:http://hogwartsrico.github.io/2018/11/11/write-a-spring/